About Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil
Documentation
Identification
- Synonyms: Japanese Peppermint Oil, Mentha Arvensis Oil, Cornmint Oil
- Botanical Name: Mentha arvensis
- Origin: India
- Plant Part: Herb
- Plant Description: There are several species of the mentha arvensis perennial herb that can grow to 3 feet in height, spreading due to their underground 'runners'. Peppermint plant has hairy leaves with serrated edges and purple spiked flowers. Peppermint Japanese is known for its high menthol content. It is so high in fact that menthol crystals sometimes form right on the leaves
- Extraction Method: Steam Distilled
The Aroma
- Aromatic Fragrance: Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil has a sharp, penetrating mint scent based on its high menthol content. The sweetness of the vapor makes it easy to see why it is such a common flavoring and scenting agent
- Aromatic Strength: Strong
- Note: Top
- Blends Well with: Basil, Bergamot, Cajeput, Cedarwood, Eucalyptus, Lemon, Lime, Mandarin, Marjoram, Niaouli, Pine, Rosemary, Spearmint and Thyme.
- Consistency: Thin
Oil Characteristics
- Natural: This essential oil is from a natural source
- Color: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Packaging: The 1/2 Oz, 2 Oz and 4 Oz each come in a single amber bottle. The 1 Lb size is in a steel canister, 10 Lb is either a single steel can or several steel canisters
Usage / Benefits
- Industries: Personal Care, Cosmetics, Aromatherapy, Home Cleaning Products, Fragrance
- Applications: Topical Application, Inhalation, Diffusion, Soap Making, Cosmetic Formulation, Perfumery
- Benefits: Cooling Sensation, Mental Clarity, Stress Relief, Soothes Skin Irritation, Promotes Respiratory Health
- Products Uses: Lotions, Balms, Massage Oils, Bath Products, Air Fresheners, Scented Candles, Aromatherapy Diffusers
- Storage: Cool, dark dry area, air tight container preferred
- Safety: Generally safe, however keep out of eyes and do not eat.
- Cautions: Not for ingestion, keep away from pets and children who may attempt to eat.
- External Use Only: Even if food grade, we do not provide items for ingestion, all of our items are for external use only.
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil: A Glimpse into its Versatility
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil, derived from the Mentha arvensis plant native to the land of the rising sun, Japan, has earned its repute as one of the most sought-after essential oils in the cosmetic and personal care industry. Although commonly recognized for its culinary and medicinal attributes, this particular strain of peppermint oil holds a myriad of benefits and applications, especially when it comes to personal care, soap making, and cosmetics.
A Distinctive Aroma
The scent profile of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil distinguishes itself with a crisp, cool, and invigorating aroma. Unlike other peppermint varieties, this particular type embodies a more refined minty note, accentuated by subtle grassy undertones. Such a unique aroma makes it a top-tier choice for fragrance formulations in a variety of cosmetic products.
Natural Cooling Properties
One of the remarkable characteristics of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is its inherent cooling sensation, attributed to its high menthol content. This innate quality makes it an invaluable ingredient in skincare and personal care products, rendering a refreshing feel upon application.
Antioxidant Richness
The natural compounds in this oil also offer a potent dose of antioxidants, vital for skin protection against environmental aggressors. These antioxidants, when incorporated into skincare products, help maintain youthful skin by counteracting oxidative stress.
Cleansing Abilities
In the realm of skincare, cleanliness is paramount. Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is well-regarded for its cleansing properties, assisting in purifying the skin, and imparting a fresh sensation. This feature makes it a staple in facial cleansers and toners.
Harmony with Other Ingredients
One of the hallmarks of an exceptional ingredient is its ability to blend harmoniously with others. Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is versatile in this regard, pairing wonderfully with a multitude of other essential oils and cosmetic ingredients, thereby enhancing the overall efficacy and aroma of products.
The Art of Soap Making
Soap artisans and enthusiasts will attest to the allure of incorporating Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil in their creations. Not only does it infuse the soap with a delightful scent, but its natural properties also contribute to a refreshing wash experience, invigorating the senses and leaving the skin feeling revitalized.
Cosmetic Innovations
In the expansive world of cosmetics, innovation is key. The introduction of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil into cosmetic formulations, from lip balms to foundations, introduces a cooling effect, a unique scent profile, and added skincare benefits. Its adaptable nature ensures it finds its place in a variety of cosmetic products, making it a favorite among formulators and consumers alike.
In Summary
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil transcends its traditional uses, marking its territory in the personal care, soap making, and cosmetic industries. Its unique aroma, combined with its myriad of beneficial properties, ensures its standing as a must-have ingredient. As with all essential oils, it's crucial to understand its potency and ensure it's used in the right concentrations to harness its full potential safely.
Expounding on the Uses of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil
Skincare Enhancer
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil, with its natural cooling and cleansing properties, has become a favorite in skincare routines. When added to face masks, cleansers, and toners, it imparts a refreshing sensation while aiding in skin purification. Moreover, its antioxidant properties play a pivotal role in anti-aging formulations, helping skin maintain its youthful vigor.
Revitalizing Bath Products
Bath bombs, salts, and oils infused with Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil transform a regular bath into a spa-like experience. The oil's invigorating aroma and cooling sensation envelop the senses, providing relaxation and rejuvenation in tandem.
Artisanal Soaps
Soap making has embraced this oil wholeheartedly. When incorporated into soap bars, it offers a distinctive scent and a cooling lather, enhancing the overall wash experience. Its cleansing properties further ensure that the skin feels clean and fresh post-use.
Hair Care Innovations
This essential oil is not limited to skincare alone. In hair care formulations, it offers a refreshing scalp sensation, making it a favored ingredient in shampoos and conditioners. Additionally, its cleansing properties assist in removing scalp impurities, promoting overall hair health.
Lip Care
Lip balms and glosses can benefit from a touch of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil. Not only does it offer a pleasant scent, but its cooling effect also provides a unique sensory experience upon application. Furthermore, its moisturizing properties ensure lips remain soft and supple.
Delving into the Main Benefits of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil, a treasure from the heart of Japan, possesses an array of advantages that have made it a highly esteemed entity in the world of essential oils. Its distinct aroma and profile, coupled with a plethora of beneficial properties, make it invaluable in numerous personal care and cosmetic applications. Below, we explore its myriad benefits in-depth.
1. Refreshing Sensation
One of the standout attributes of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is its innate cooling property, primarily due to its high menthol content. This characteristic imparts a refreshing sensation upon topical application, ideal for products aimed at providing relief from heat or for invigorating the senses.
2. Deep Cleansing Properties
Known for its deep cleansing abilities, this oil is adept at purifying skin and scalp, eliminating impurities, and leaving behind a clean, fresh feel. This makes it a popular choice in facial cleansers, toners, and shampoos.
3. Rich in Antioxidants
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil boasts a robust antioxidant profile, vital in combating harmful free radicals. This makes it a prime ingredient in skincare products aiming to protect skin against environmental stressors and premature aging.
4. Natural Moisturizer
Though not as pronounced as its other features, the moisturizing qualities of this oil are noteworthy. It helps in retaining skin's natural moisture, ensuring it remains hydrated and supple, which is particularly beneficial in lip care products and lotions.
5. Enhanced Mental Alertness
The invigorating aroma of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is believed to stimulate the mind, enhancing mental alertness and concentration. This makes it an essential oil of choice for aromatherapy sessions aiming to boost focus and cognitive functions.
6. Harmonious Blending
The oil's versatile nature allows it to blend seamlessly with a multitude of other essential oils and cosmetic ingredients. This adaptability not only enhances the overall efficacy of products but also introduces a balanced and layered scent profile.
7. Aromatherapeutic Benefits
Apart from its tangible skin and hair benefits, Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is also known for its mood-enhancing properties. Its aroma has been associated with reduced feelings of tension and promoting a sense of calm and relaxation.
8. Enhances Product Experience
Its inclusion in cosmetic and personal care products adds an elevated sensory experience for users, thanks to its signature cooling effect and distinctive aroma. This makes products more appealing and adds a touch of luxury.
Conclusion
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is more than just a fragrant addition; its plethora of benefits, ranging from skin care to mental well-being, marks its position as an indispensable asset in the world of personal care and cosmetics. As with all essential oils, it's imperative to ensure that it's used in appropriate concentrations and blends to fully harness its potential safely.
Principal Constituents of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil
The efficacy and characteristic attributes of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil can be traced back to its rich chemical profile. Understanding these principal constituents provides insights into the oil's multifaceted benefits.
1. Menthol
Menthol is arguably the most prominent component in Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil. Responsible for the oil's characteristic cooling sensation, it also offers cleansing properties and plays a vital role in providing that refreshing feel upon application.
2. Menthone
A significant constituent, menthone contributes to the oil's distinct aroma. It complements menthol in providing the oil's refreshing characteristics and plays a role in its therapeutic properties.
3. 1,8-Cineole
Also known as eucalyptol, 1,8-cineole is known for its soothing properties and contributes to the oil's overall scent profile.
4. Menthyl Acetate
This constituent introduces a sweet undertone to the oil's aroma and enhances its natural cooling properties.
5. Limonene
Present in many essential oils, limonene adds a hint of citrusy note to the aroma and is known for its uplifting effects.
Conclusion
The multifaceted benefits of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil are intrinsically linked to its rich chemical profile. These constituents, each with its unique properties, collectively contribute to the oil's revered status in the realm of personal care and cosmetics.
What Are the Effects of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil on Pets?
While essential oils are often hailed for their multitude of benefits for humans, it's important to note that what is beneficial for humans may not be for pets. The metabolism and physiology of animals differ greatly from those of humans, and it's crucial to keep this in mind when using oils like Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil around pets.
Dogs and cats have a heightened sense of smell, which can make strong oils like peppermint overwhelming for them. In particular, peppermint oil contains menthol, which can be irritating for animals when inhaled. While some pet owners use diluted peppermint oil as a flea repellent or to treat certain skin conditions, it is imperative to consult a qualified veterinarian before attempting to use this oil on or around pets.
Ingesting even small amounts of peppermint oil can be toxic for animals, leading to symptoms such as lethargy, vomiting, and diarrhea. Additionally, applying peppermint oil directly onto your pet's skin can result in burns or irritation, especially if the oil is not adequately diluted.
In summary, while peppermint oil has its uses, extreme caution should be exercised when considering its use around pets. Always consult a veterinarian for advice tailored to your specific animal's needs.
What Is the Role of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil in Aromatherapy?
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is a popular choice in the world of aromatherapy for its invigorating and refreshing qualities. This essential oil is known for its high menthol content, which provides a cooling sensation and can help to clear the respiratory tract. These attributes make it a preferred oil for revitalizing the body and mind, and for aiding in mental clarity.
In aromatherapy, Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is often used in diffusers to promote an atmosphere of focus and energy. It blends well with other essential oils such as lavender, eucalyptus, and rosemary, offering synergistic effects that can amplify its benefits. The diffused aroma of peppermint can act as a natural stress reliever, and many find that it helps them concentrate better during tasks that require mental acuity.
Additionally, this essential oil is often incorporated into topical applications like massage oils and balms used in aromatherapeutic settings. When applied to the skin in a diluted form, it provides a refreshing, tingling sensation, often helping to relieve minor aches and improve circulation.
As with any essential oil, it's crucial to use Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil responsibly. Always dilute it appropriately and ensure you're using a high-quality, pure product. People with sensitive skin or certain medical conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using peppermint oil in aromatherapy practices.
What Is the History of Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil?
Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil, derived from the Mentha arvensis plant, has a rich history that spans across various cultures and continents. While peppermint, in general, is native to Europe and the Middle East, Mentha arvensis is particularly prevalent in the Asian continent, especially in Japan. The plant has been cultivated and utilized in traditional Japanese medicine for its multiple benefits, such as digestive aids and respiratory relief, long before it became commercialized.
The use of peppermint and its essential oil in Japan is deeply intertwined with the country's historical practices in herbal medicine, called Kampo. It has been documented in ancient texts and remains a vital component of various traditional remedies. Besides medicinal uses, this particular variety of peppermint oil has also been used in Japanese ceremonies and spiritual practices, often to cleanse the atmosphere and ward off negative energies.
With the globalization of essential oils and natural remedies, Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil has found its way into homes and practices worldwide. Its unique chemical composition, distinct from other types of peppermint oils, gives it a special place in aromatherapy and other holistic health practices. Its historical roots in Japanese culture and medicine only add to its allure and effectiveness.
Are There Any Additional Safety Concerns with Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil?
While Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil is widely regarded for its various benefits, it's essential to be aware of safety considerations. This oil contains a high concentration of menthol, which can be extremely potent. Inappropriate use can lead to adverse reactions like skin irritation, allergic responses, and digestive issues if ingested.
Children and pregnant or nursing women should avoid using this oil unless advised by a healthcare provider. Due to its high menthol content, it may interfere with certain medications and medical conditions, particularly those related to the respiratory system and digestive tract.
It is crucial to dilute Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil adequately before topical application to avoid skin irritation or burns. A patch test is advisable to check for any allergic reactions. Additionally, the oil should not be applied to or near the face of infants or young children, as it could cause spasms that might affect breathing.
Lastly, while it may be tempting to ingest this essential oil for its digestive benefits, this should never be done without professional medical advice. In summary, while Peppermint Japanese Essential Oil offers a multitude of advantages, it should be used cautiously, respecting its potency and potential for adverse effects.
FAQ
Why Is Peppermint Good for the Lungs?
Peppermint has long been recognized for its beneficial effects on the respiratory system. One of the primary active components of peppermint is menthol, which acts as a natural bronchodilator. It helps to open up the airways, making it easier to breathe. Menthol's cooling effect can also soothe irritation in the throat and lungs, providing relief from coughing and other respiratory discomforts.
Beyond menthol, peppermint contains various antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that may contribute to lung health. The oil has been traditionally used in steam inhalations and diffusers to aid in clearing congestion, relieving symptoms of asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory issues. When inhaled, the vapors from peppermint essential oil can help dislodge mucus and reduce inflammation, facilitating easier breathing.
It is essential to note that while peppermint can offer symptomatic relief for various respiratory conditions, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of respiratory issues, especially for individuals who have chronic lung conditions or are using other medications.
The Artisan's Choice for Soap and Cosmetic Ingredients
In the expansive world of online retail, there exists a unique niche for hobbyists and professionals alike: soap and cosmetic making. One standout in this niche is our store, SoapGoods.com.
SoapGoods is an online-only retailer that has carved out a space in the market by catering to the specific needs of those passionate about handcrafted soap, skincare, and cosmetics. Offering an array of high-quality ingredients and supplies, SoapGoods aims to be a one-stop-shop for everything needed to create personal care items, from the basic to the most intricate.
Products
The product range at SoapGoods is vast and encompasses a wide variety of categories. Here are some of the main ones:
- Oils and Butters: Fundamental to soap-making, oils and butters like olive oil pomace, coconut oil 76, shea butter refined, and cocoa butter natural provide the base for many formulations. Each oil or butter possesses unique properties, be it moisturizing capabilities, lathering quality, or hardness.
- Essential Oils and Fragrance Oils: To give handmade soaps and cosmetics their distinctive scents, SoapGoods offers a diverse selection of essential oils derived from natural plants and fragrance oils which are more complex, synthetic scents.
- Additives: From natural clays and botanicals to exfoliating agents like pumice and walnut shell, these additives help enhance the texture, appearance, and benefits of the final product.
- Colorants: SoapGoods provides a range of pigments, dyes, and micas, allowing crafters to achieve the perfect hue for their creations.
- Molds and Equipment: Beyond ingredients, SoapGoods stocks a variety of tools and equipment. Silicone molds, thermometers, pH testers, and more ensure that hobbyists and professionals can craft their products with precision.
- Packaging Supplies: For those looking to sell or gift their creations, the store offers an assortment of packaging materials, including bottles, jars and shrink wraps.
Quality and Sourcing
One of the standout features of SoapGoods is its commitment to quality. Many products are sourced to ensure they are non-GMO, and from reputable sources. After 20 years in the industry, we have been able to find the highest quality sources at fair prices. This dedication to quality resonates with a clientele that values natural and ethical ingredients.
User Experience
Shopping on SoapGoods.com is a seamless experience. The site is intuitively designed, making product searches straightforward. Clear product descriptions, accompanied by high-resolution images, make it easier for shoppers to discern the right products for their needs. Moreover, the site often features customer reviews, which offer insights and real-world experiences with the products.
Shipping and Customer Service
With efficient shipping options and the fastest shipping in the industry, SoapGoods ensures that customers receive their orders in a timely manner. Their commitment to customer satisfaction is also evident in their attentive customer service, ready to address any queries or concerns.
FedEx Delivery Map
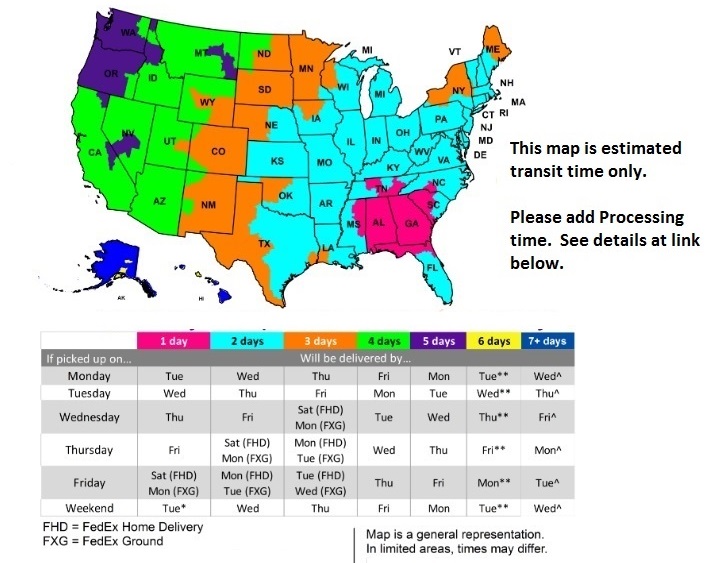
For Processing Times Click Here
USPS Delivery Map
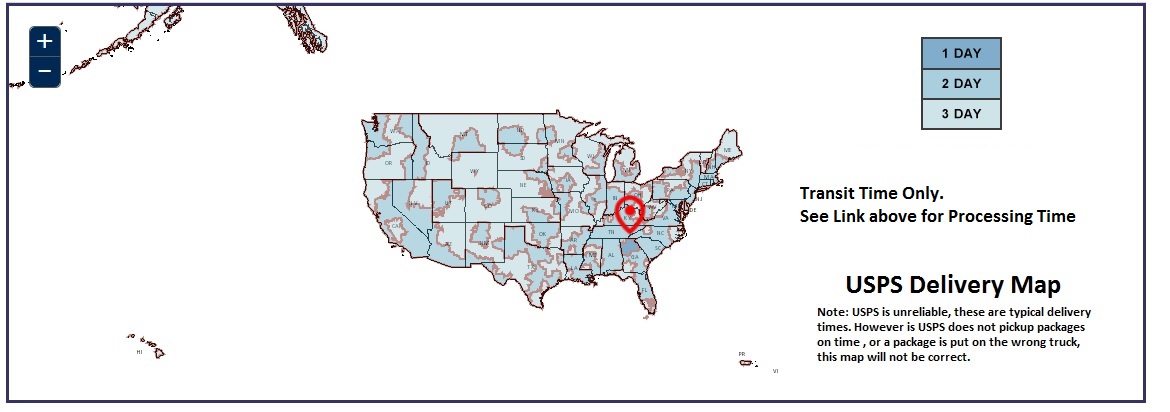
Typical Delivery Times to Major US Cities
| Major Cities | Total Business Days +1 / -1 |
|---|---|
| Alabama (AL) - Montgomery, Birmingham | 1 |
| Alaska (AK) - Juneau, Anchorage | 7 |
| Arizona (AZ) - Phoenix, Tucson | 4 |
| Arkansas (AR) - Little Rock, Fayetteville | 2 |
| California (CA) - Sacramento, Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego, Sacramento, San Jose | 4 |
| Colorado (CO) - Denver, Colorado Springs | 3 |
| Connecticut (CT) - Hartford, New Haven | 2 |
| Delaware (DE) - Dover, Wilmington, Newark | 2 |
| Florida (FL) - Tallahassee, Orlando, Miami, Jacksonville, Tampa, Destin | 2 |
| Georgia (GA) - Atlanta, Savannah, Augusta, Athens | 1 |
| Hawaii (HI) - Honolulu, Kailua | 7 |
| Idaho (ID) - Boise, Coeur d'Alene | 4 |
| Illinois (IL) - Springfield, Chicago, Peoria, Rockford | 2 |
| Indiana (IN) - Indianapolis, Fort Wayne | 2 |
| Iowa (IA) - Des Moines, Cedar Rapids | 2 |
| Kansas (KS) - Topeka, Wichita, Kansas City | 2 |
| Kentucky (KY) - Frankfort, Louisville, Lexington | 2 |
| Louisiana (LA) - Baton Rouge, New Orleans, Lafayette | 2 |
| Maine (ME) - Augusta, Portland, Bangor | 3 |
| Maryland (MD) - Annapolis, Baltimore | 2 |
| Massachusetts (MA) - Boston, Cambridge, Worcester | 2 |
| Michigan (MI) - Lansing, Detroit, Grand Rapids | 2 |
| Minnesota (MN) - St. Paul, Minneapolis, Duluth | 3 |
| Mississippi (MS) - Jackson, Biloxi, Hattiesburg | 1 |
| Missouri (MO) - Jefferson City, St Louis, Kansas City | 2 |
| Montana (MT) - Helena, Billings | 4 |
| Nebraska (NE) - Lincoln, Omaha | 2 |
| Nevada (NV) - Carson City, Las Vegas, Reno | 4 |
| New Hampshire (NH) - Concord, Manchester, Portsmouth | 2 |
| New Jersey (NJ) - Trenton, Newark, Jersey City | 2 |
| New Mexico (NM) - Santa Fe, Alburquerque | 3 |
| New York (NY) - Albany, New York, Rochester, Buffalo, Albany, Syracuse, Niagara Falls, Ithaca | 3 |
| North Carolina (NC) - Raleigh, Charlotte | 2 |
| North Dakota (ND) - Bismarck, Fargo | 3 |
| Ohio (OH) - Columbus, Cleveland, Cincinnati | 2 |
| Oklahoma (OK) - Oklahoma City, Fairview, | 2 |
| Oregon (OR) - Salem, Portland, Eugene | 5 |
| Pennsylvania (PA) - Harrisburg, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh | 2 |
| Rhode Island (RI) - Providence, Newport | 2 |
| South Carolina (SC) - Columbia, Charleston | 1 |
| South Dakota (SD) - Pierre, Sioux Falls, Rapid City | 3 |
| Tennessee (TN) - Nashville, Memphis | 2 |
| Texas (TX) - Austin, Houston, Dallas | 3 |
| Utah (UT) - Salt Lake City, St. George | 3 |
| Vermont (VT) - Montpelier, Burlington | 3 |
| Virginia (VA) - Richmond, Virginia Beach | 2 |
| Washington (WA) - Olympia, Seattle, Vancouver, Spokane | 5 |
| West Virginia (WV) - Charleston, Morgantown | 2 |
| Wisconsin (WI) - Madison, Milwaukee | 2 |
| Wyoming (WY) - Cheyenne, Jackson | 4 |
Disclaimer: All product descriptions and specifications provided in this description are intended as a guide only and are subject to change without notice. While we strive for accuracy, discrepancies or errors may be present. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Customer reviews
Recommendation for purchase
Will be using this in a lot of different ways !"
i can no longer find and I was not impressed. It smells ...
Will be using this in a lot of different ways !"
i can no longer find and I was not impressed. It smells ...











