About Thyme Red Essential Oil
Documentation
Identification
- Synonyms: Red Thyme Oil, Thymus vulgaris Oil, Common Thyme Red Oil
- Botanical Name: Thymus vulgaris
- Origin: India or Hungary
- Plant Part: Leaves
- Plant Description: The Thyme plant is an evergreen perennial shrub that grows up to 45 cm (18 inches) in height. It has a woody root system, a multi-branched stem, small elliptical greenish gray aromatic leaves and pale purple or white flowers. Thyme is derived from the Greek word 'thymos' that means 'perfume'. White Thyme can also be derived from this species if the Red Thyme is further distilled; nonetheless, White Thyme is more commonly derived from the Thymus Zygis species.
- Extraction Method: Steam Distilled
The Aroma
- Aromatic Fragrance: Red Thyme Essential Oil has a fresh, herbaceous, medicinal scent. It has often been described as sharp and warming
- Aromatic Strength: Medium
- Note: Middle
- Blends Well with: Bergamot, Grapefruit, Lemon, Lavender, Rosemary and Pine
- Consistency: Thin
Oil Characteristics
- Natural: This essential oil is from a natural source
- Color: Pale yellow to reddish yellow clear liquid
- Packaging: The 1/2 Oz, 2 Oz and 4 Oz each come in a single amber bottle. The 1 Lb size is in a steel canister, 10 Lb is either a single steel can or several steel canisters
Usage / Benefits
- Industries: Personal Care, Cosmetics, Aromatherapy, Soap Making, Fragrance, Cleaning Products, Essential Oil Blends
- Applications: Skin Care Products, Hair Care Products, Aromatherapy Blends, Soaps, Perfumes, Cleaning Agents, Scent Diffusers, Massage Oils
- Benefits: Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, Mood Uplifting, Stress Reducing, Skin Toning, Aromatherapeutic, Muscle Soothing
- Products Uses: Facial Serums, Shampoos, Conditioners, Body Lotions, Hand Creams, Soaps, Room Sprays, Scent Diffuser Blends, Massage Oils, Cleaning Solutions
- Storage: Cool, dark dry area, air tight container preferred
- Safety: Generally safe, however keep out of eyes and do not eat.
- Cautions: Not for ingestion, keep away from pets and children who may attempt to eat.
- External Use Only: Even if food grade, we do not provide items for ingestion, all of our items are for external use only.
Thyme Red Essential Oil: A Deep Dive into Its Charm
Thyme Red Essential Oil, derived from the steam distillation of the Thymus vulgaris plant's flowering tops and leaves, has firmly established itself within the realm of personal care and cosmetics. Beyond the kitchen, where it's commonly recognized as a culinary herb, thyme's potent aroma and myriad of benefits have been harnessed in various beauty and wellness products, making it a favorite among enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Origins and Extraction
Thyme, a perennial herb native to the Mediterranean region, has a rich history dating back millennia. The ancient Egyptians used it for embalming, while the Greeks burned it as incense in their temples. The essential oil, particularly the red variant, is extracted through a steam distillation process, ensuring the preservation of its potent constituents.
Appearance and Aroma
Thyme Red Essential Oil boasts a reddish-brown hue, differing from its white counterpart. Its aroma is potent, herbaceous, and slightly spicy, making it a robust additive in various formulations.
A Rich Composition
The oil's efficacy in personal care is largely attributed to its chemical constituents. Rich in thymol, carvacrol, and p-cymene, among others, Thyme Red Essential Oil possesses properties that are highly coveted in the beauty industry.
The Bridge to Modern Personal Care
The transition of thyme from ancient rituals to modern personal care products is a testament to its enduring appeal and efficacy. The skincare and beauty industry, always on the hunt for potent, natural ingredients, has embraced Thyme Red Essential Oil for its unique properties.
Skincare Virtues
Thyme Red Essential Oil has been known to support skin health. It's often integrated into creams, lotions, and serums, targeting a range of skin concerns. Its properties make it a beneficial ingredient for maintaining a clear and vibrant complexion.
Integration in Haircare
From shampoos to conditioners, Thyme Red Essential Oil is a favorite. Its ability to support a healthy scalp, combined with its aromatic appeal, makes it a staple in many haircare formulations.
The Cosmetic Arena
In the realm of cosmetics, the oil's potent aroma is a game-changer. It lends a refreshing scent to products, enhancing the sensory experience. Moreover, its properties can be harnessed in lip balms, natural deodorants, and other cosmetic preparations.
Soap Making: An Artistic Endeavor
Soap makers adore Thyme Red Essential Oil for the distinct hue and aroma it imparts. Natural, handmade soaps infused with this oil not only cleanse but also offer an invigorating bathing experience. The oil's constituents also lend certain properties that are cherished in the soap-making community.
In summary, Thyme Red Essential Oil, with its rich history and versatile applications, has etched an indelible mark in the personal care and cosmetics industry. Its blend of aromatic allure and beneficial properties make it an ingredient of choice for those looking to merge wellness with beauty.
Delving into the Uses of Thyme Red Essential Oil
Thyme Red Essential Oil's diverse range of applications within personal care and cosmetic formulations showcases its versatility and potency. Let's delve deeper into its multifaceted uses.
1. Skin Elixirs
Thyme Red Essential Oil's properties make it a sought-after ingredient in serums and elixirs meant for skin rejuvenation. Its ability to support skin clarity and health ensures it has a place in various formulations targeting diverse skin concerns.
2. Hair and Scalp Treatments
The oil's efficacy extends to haircare. When incorporated into shampoos, conditioners, or hair masks, it can offer a revitalizing effect, supporting scalp health and enhancing hair's natural shine and vitality.
3. Handmade Soaps
Artisanal soap makers appreciate the unique touch Thyme Red Essential Oil brings to their creations. The oil's rich hue and invigorating scent elevate the sensory experience of the soap, making each bath a refreshing ritual.
4. Fragrance Crafting
Given its robust aroma, Thyme Red Essential Oil often finds its way into natural perfumes and deodorants. It can serve as a middle note in fragrance blends, adding a layer of complexity and depth to the overall scent profile.
5. Bath and Spa Products
The relaxing and invigorating properties of Thyme Red Essential Oil make it a favorite in bath bombs, salts, and spa products. These products aim to transform the mundane bathing routine into a therapeutic, spa-like experience.
6. Lotions and Body Butters
For those looking to craft nourishing skin formulations, Thyme Red Essential Oil is a boon. Its addition to lotions
What Are the Main Benefits of Thyme Red Essential Oil?
Thyme Red Essential Oil is a potent and versatile natural substance that offers a wide range of benefits, primarily in the realms of personal care, cosmetic making, and aromatherapy. Below are some of the key benefits that make this essential oil a popular choice in various industries.
Antimicrobial Properties
Thyme Red Essential Oil has strong antimicrobial properties, making it effective in controlling the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi. These characteristics make the oil an excellent addition to skin care and hair care formulations, where it can act as a natural preservative and protective agent.
Antioxidant Benefits
The oil is rich in antioxidants that help combat free radicals, which are the primary cause of premature aging. When used in skin care products, Thyme Red Essential Oil can help reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Thyme Red Essential Oil has anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate skin conditions like acne, eczema, and dermatitis. Its soothing effect on the skin also makes it beneficial in formulations intended for sensitive or irritated skin.
Mood Uplifting and Stress Reduction
In the realm of aromatherapy, the oil is known for its mood-uplifting and stress-reducing effects. When diffused, it can create a calming atmosphere that helps relieve anxiety, stress, and depression.
Skin Toning
When used in skin care routines, the oil can act as a natural toner, helping to tighten and firm the skin. This is particularly useful in anti-aging products where a toned appearance is desired.
Aromatherapeutic Uses
The aromatic profile of Thyme Red Essential Oil also makes it popular in aromatherapy blends. Whether used alone or in combination with other essential oils, its rich, herbaceous aroma can provide a sensory experience that is both invigorating and comforting.
Muscle Soothing
Due to its anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic properties, Thyme Red Essential Oil is beneficial in massage oils aimed at relieving muscle tension and soreness. Its warming effect on the skin makes it particularly effective for use in sports recovery blends.
What Are the Principal Constituents of Thyme Red Essential Oil?
Thyme Red Essential Oil is a complex blend of phytochemicals, each contributing to its range of beneficial properties. Some of the principal constituents include:
Thymol
Thymol is the primary active component in Thyme Red Essential Oil and is responsible for its strong antimicrobial and antifungal properties. This constituent is commonly used in natural preservatives and disinfectants.
Carvacrol
Carvacrol is another significant component that also has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. It enhances the oil's efficacy in combating various pathogens and oxidative stress.
Linalool and Limonene
These terpenes contribute to the oil's aromatic profile and have their own set of benefits, including stress reduction and mood uplifting effects.
Cineole
Cineole is known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, making it useful in formulations that aim to relieve pain and inflammation.
Understanding the principal constituents of Thyme Red Essential Oil helps in appreciating its multifaceted benefits and applications. It also assists formulators in creating products that effectively harness the full potential of this powerful essential oil.
What Are the Effects of Thyme Red Essential Oil on Pets?
Thyme Red Essential Oil, although beneficial for humans, may not have the same positive effects on pets and could even pose certain risks. As such, it's crucial to approach its use around pets with caution.
High Thymol Content
The oil contains a high concentration of thymol, which can be toxic if ingested by pets like dogs and cats. Even skin contact or inhalation can be problematic. Symptoms of thymol toxicity in pets can include drooling, vomiting, and lethargy.
Respiratory Issues
Pets, particularly cats, have a sensitive respiratory system, and the strong aroma of Thyme Red Essential Oil could trigger respiratory discomfort or allergies. Signs can include coughing, sneezing, and shortness of breath.
Skin Irritation
The oil can also cause skin irritations in pets. If it comes into contact with their skin, it may cause redness, itching, and discomfort.
Precautions and Consultation
Given these potential risks, it's advisable to consult with a veterinarian before using Thyme Red Essential Oil in an environment where pets are present. Make sure to store the oil in a place that is inaccessible to your pets and never apply it directly to their skin or add it to their food or water without professional advice.
What Is the Aromatherapy Aspect of Thyme Red Essential Oil?
In the realm of aromatherapy, Thyme Red Essential Oil is known for its potent aromatic properties and multi-faceted benefits. It has a warm, herbaceous scent that can both stimulate the senses and calm the mind.
Stress Reduction and Mental Clarity
The essential oil is often used in aromatherapy practices for its ability to alleviate stress and promote mental clarity. When diffused in the air, its scent can have a calming effect on the mind, helping to reduce anxiety and foster a sense of wellbeing.
Mood Enhancement
The oil's aroma is also effective in lifting the mood and invigorating the spirit. Some users find that diffusing Thyme Red Essential Oil can result in an uplifting experience that helps to dispel feelings of sadness or emotional fatigue.
Complementary Blends
Thyme Red Essential Oil pairs well with other essential oils such as lavender, cedarwood, and rosemary, thereby creating synergistic blends that enhance its aromatherapeutic properties. Such combinations can be used in diffusers or added to massage oils for an enriched sensory experience.
A Word of Caution
While the aromatic benefits of Thyme Red Essential Oil are extensive, it's crucial to dilute the oil properly and conduct a patch test to avoid skin irritation or allergic reactions. Consulting an aromatherapy expert or healthcare provider for appropriate usage guidelines is highly recommended.
The Historical Tapestry of Thyme Red Essential Oil
Thyme Red Essential Oil, extracted from the Thymus vulgaris plant, carries with it a rich tapestry of history that spans several cultures and epochs. A true testament to the herb's enduring allure, its journey through time is as aromatic as the oil itself.
Antiquity and the Mediterranean Roots
Thyme's tale begins in the Mediterranean, where its parent plant was considered a symbol of bravery and courage. The ancient Greeks held thyme in high esteem, using it for both medicinal and ceremonial purposes. They would often burn it as incense in their sacred temples. Soldiers were also given sprigs of thyme as a symbol of courage before heading into battle.
Pharaohs and Embalming Rituals
Traveling across to ancient Egypt, thyme held a different yet equally significant role. The Egyptians utilized the herb during the intricate process of mummification. Thyme's antiseptic properties made it invaluable in the preservation of the Pharaohs, ensuring their passage to the afterlife was unblemished.
Medieval Times and Folklore
In medieval Europe, thyme continued its association with bravery. Knights would often wear scarves embroidered with thyme as they rode into battle. Moreover, thyme became a staple in folk medicine and was often kept in households to ward off illnesses and evil spirits.
The eventual distillation of Thyme Red Essential Oil brought about a more concentrated form of its benefits and uses, creating an essence that has since become a staple in various applications, from personal care to aromatherapy.
Thus, Thyme Red Essential Oil's journey, from ancient Mediterranean fields to modern apothecary shelves, reflects the timeless appeal and multifaceted benefits of this aromatic gem.
Proceed with Caution: Safety Concerns of Thyme Red Essential Oil
While Thyme Red Essential Oil boasts numerous benefits, it's equally vital to be aware of its safety implications. Being a potent essence, this oil demands careful handling and usage.
1. Skin Sensitization
Due to its high thymol content, Thyme Red Essential Oil can be irritating to some individuals, especially those with sensitive skin. It's paramount to conduct a patch test before full-scale application. Moreover, always dilute the oil with a carrier oil to minimize potential skin reactions.
2. Not Suitable for All
Pregnant and nursing women, as well as young children, should exercise caution. It's recommended to consult a healthcare professional before using the oil in such cases.
3. Potential Drug Interactions
Individuals on medication, especially anticoagulants or major surgery patients, should be wary. Thyme Red Essential Oil might interfere with blood clotting. Always consult with a healthcare provider if you're on medication or have underlying health conditions.
4. Ingestion Concerns
Even though it's derived from a culinary herb, the concentrated nature of Thyme Red Essential Oil makes it unsuitable for internal consumption unless guided by a qualified professional.
While Thyme Red Essential Oil is a treasure trove of benefits, it demands respect and careful handling. Awareness of its safety concerns ensures that you harness its advantages while minimizing potential risks.
FAQ
The Artisan's Choice for Soap and Cosmetic Ingredients
In the expansive world of online retail, there exists a unique niche for hobbyists and professionals alike: soap and cosmetic making. One standout in this niche is our store, SoapGoods.com.
SoapGoods is an online-only retailer that has carved out a space in the market by catering to the specific needs of those passionate about handcrafted soap, skincare, and cosmetics. Offering an array of high-quality ingredients and supplies, SoapGoods aims to be a one-stop-shop for everything needed to create personal care items, from the basic to the most intricate.
Products
The product range at SoapGoods is vast and encompasses a wide variety of categories. Here are some of the main ones:
- Oils and Butters: Fundamental to soap-making, oils and butters like olive oil pomace, coconut oil 76, shea butter refined, and cocoa butter natural provide the base for many formulations. Each oil or butter possesses unique properties, be it moisturizing capabilities, lathering quality, or hardness.
- Essential Oils and Fragrance Oils: To give handmade soaps and cosmetics their distinctive scents, SoapGoods offers a diverse selection of essential oils derived from natural plants and fragrance oils which are more complex, synthetic scents.
- Additives: From natural clays and botanicals to exfoliating agents like pumice and walnut shell, these additives help enhance the texture, appearance, and benefits of the final product.
- Colorants: SoapGoods provides a range of pigments, dyes, and micas, allowing crafters to achieve the perfect hue for their creations.
- Molds and Equipment: Beyond ingredients, SoapGoods stocks a variety of tools and equipment. Silicone molds, thermometers, pH testers, and more ensure that hobbyists and professionals can craft their products with precision.
- Packaging Supplies: For those looking to sell or gift their creations, the store offers an assortment of packaging materials, including bottles, jars and shrink wraps.
Quality and Sourcing
One of the standout features of SoapGoods is its commitment to quality. Many products are sourced to ensure they are non-GMO, and from reputable sources. After 20 years in the industry, we have been able to find the highest quality sources at fair prices. This dedication to quality resonates with a clientele that values natural and ethical ingredients.
User Experience
Shopping on SoapGoods.com is a seamless experience. The site is intuitively designed, making product searches straightforward. Clear product descriptions, accompanied by high-resolution images, make it easier for shoppers to discern the right products for their needs. Moreover, the site often features customer reviews, which offer insights and real-world experiences with the products.
Shipping and Customer Service
With efficient shipping options and the fastest shipping in the industry, SoapGoods ensures that customers receive their orders in a timely manner. Their commitment to customer satisfaction is also evident in their attentive customer service, ready to address any queries or concerns.
FedEx Delivery Map
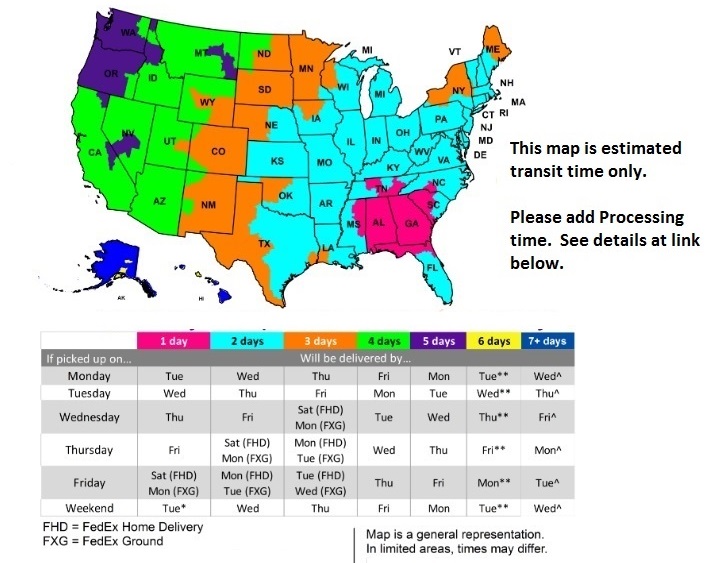
For Processing Times Click Here
USPS Delivery Map
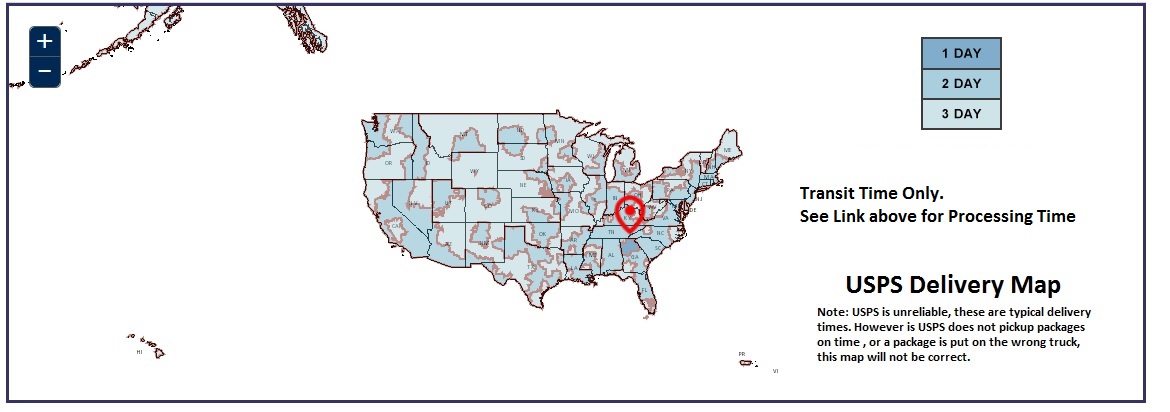
Typical Delivery Times to Major US Cities
| Major Cities | Total Business Days +1 / -1 |
|---|---|
| Alabama (AL) - Montgomery, Birmingham | 1 |
| Alaska (AK) - Juneau, Anchorage | 7 |
| Arizona (AZ) - Phoenix, Tucson | 4 |
| Arkansas (AR) - Little Rock, Fayetteville | 2 |
| California (CA) - Sacramento, Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego, Sacramento, San Jose | 4 |
| Colorado (CO) - Denver, Colorado Springs | 3 |
| Connecticut (CT) - Hartford, New Haven | 2 |
| Delaware (DE) - Dover, Wilmington, Newark | 2 |
| Florida (FL) - Tallahassee, Orlando, Miami, Jacksonville, Tampa, Destin | 2 |
| Georgia (GA) - Atlanta, Savannah, Augusta, Athens | 1 |
| Hawaii (HI) - Honolulu, Kailua | 7 |
| Idaho (ID) - Boise, Coeur d'Alene | 4 |
| Illinois (IL) - Springfield, Chicago, Peoria, Rockford | 2 |
| Indiana (IN) - Indianapolis, Fort Wayne | 2 |
| Iowa (IA) - Des Moines, Cedar Rapids | 2 |
| Kansas (KS) - Topeka, Wichita, Kansas City | 2 |
| Kentucky (KY) - Frankfort, Louisville, Lexington | 2 |
| Louisiana (LA) - Baton Rouge, New Orleans, Lafayette | 2 |
| Maine (ME) - Augusta, Portland, Bangor | 3 |
| Maryland (MD) - Annapolis, Baltimore | 2 |
| Massachusetts (MA) - Boston, Cambridge, Worcester | 2 |
| Michigan (MI) - Lansing, Detroit, Grand Rapids | 2 |
| Minnesota (MN) - St. Paul, Minneapolis, Duluth | 3 |
| Mississippi (MS) - Jackson, Biloxi, Hattiesburg | 1 |
| Missouri (MO) - Jefferson City, St Louis, Kansas City | 2 |
| Montana (MT) - Helena, Billings | 4 |
| Nebraska (NE) - Lincoln, Omaha | 2 |
| Nevada (NV) - Carson City, Las Vegas, Reno | 4 |
| New Hampshire (NH) - Concord, Manchester, Portsmouth | 2 |
| New Jersey (NJ) - Trenton, Newark, Jersey City | 2 |
| New Mexico (NM) - Santa Fe, Alburquerque | 3 |
| New York (NY) - Albany, New York, Rochester, Buffalo, Albany, Syracuse, Niagara Falls, Ithaca | 3 |
| North Carolina (NC) - Raleigh, Charlotte | 2 |
| North Dakota (ND) - Bismarck, Fargo | 3 |
| Ohio (OH) - Columbus, Cleveland, Cincinnati | 2 |
| Oklahoma (OK) - Oklahoma City, Fairview, | 2 |
| Oregon (OR) - Salem, Portland, Eugene | 5 |
| Pennsylvania (PA) - Harrisburg, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh | 2 |
| Rhode Island (RI) - Providence, Newport | 2 |
| South Carolina (SC) - Columbia, Charleston | 1 |
| South Dakota (SD) - Pierre, Sioux Falls, Rapid City | 3 |
| Tennessee (TN) - Nashville, Memphis | 2 |
| Texas (TX) - Austin, Houston, Dallas | 3 |
| Utah (UT) - Salt Lake City, St. George | 3 |
| Vermont (VT) - Montpelier, Burlington | 3 |
| Virginia (VA) - Richmond, Virginia Beach | 2 |
| Washington (WA) - Olympia, Seattle, Vancouver, Spokane | 5 |
| West Virginia (WV) - Charleston, Morgantown | 2 |
| Wisconsin (WI) - Madison, Milwaukee | 2 |
| Wyoming (WY) - Cheyenne, Jackson | 4 |
Disclaimer: All product descriptions and specifications provided in this description are intended as a guide only and are subject to change without notice. While we strive for accuracy, discrepancies or errors may be present. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Customer reviews
Recommendation for purchase











